 DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point) is a series of bits in the IP header for classification purposes. These bits specify the precedence value of the packet, the drop probability, and the network service used.
DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point) is a series of bits in the IP header for classification purposes. These bits specify the precedence value of the packet, the drop probability, and the network service used.
Before setting the DSCP flag with a desired value, you need to take some things into consideration. You cannot force the DSCP flag from the Data Distribution Service (DDS) middleware, but you can suggest the system use a specific value. The reason is that all network elements such as switches and routers must have the capability and be enabled to actually use the TOS bits to treat higher-priority packets differently (TOS is an older mechanism to prioritize packets). In addition, many network transports are not capable of managing packet priority. All this makes it impossible for DDS to control the prioritization of data at the network level.
If you want to suggest a DSCP value to your system, you should use the transport_priority QoS parameter. But if you want to change the metadata packets, you need to use the metatraffic_transport_priority QoS parameter.
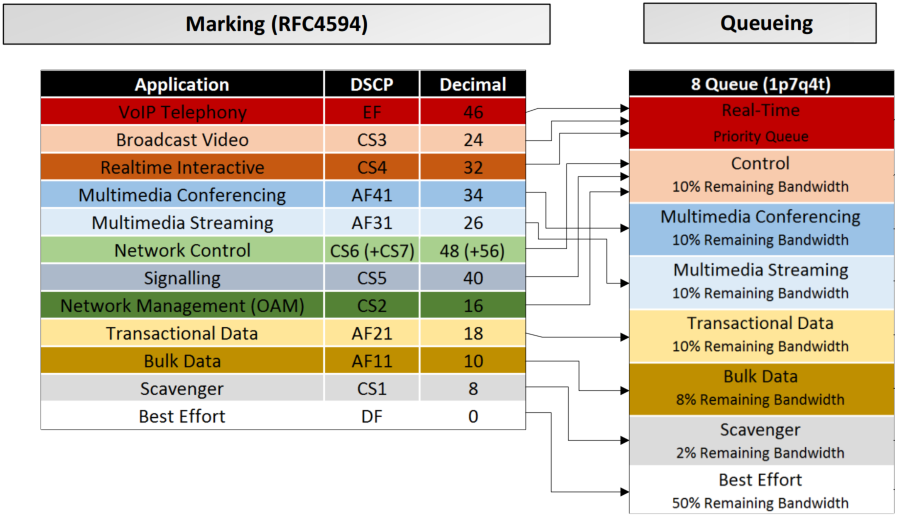
Notice that the DSCP can have different values:
| DSCP Value | Decimal Value | Meaning | Drop Probability | Equivalent IP Precedence Value |
| 101 110 | 46 | High Priority
Expedited Forwarding (EF) |
N/A | 101 – Critical |
| 000 000 | 0 | Best Effort | N/A | 000 – Routine |
| 001 010 | 10 | AF11 | Low | 001 – Priority |
| 001 100 | 12 | AF12 | Medium | 001 – Priority |
| 001 110 | 14 | AF13 | High | 001 – Priority |
| 010 010 | 18 | AF21 | Low | 010 – Immediate |
| 010 100 | 20 | AF22 | Medium | 010 – Immediate |
| 010 110 | 22 | AF23 | High | 010 – Immediate |
| 011 010 | 26 | AF31 | Low | 011 – Flash |
| 011 100 | 28 | AF32 | Medium | 011 – Flash |
| 011 110 | 30 | AF33 | High | 011 – Flash |
| 100 010 | 34 | AF41 | Low | 100 – Flash Override |
| 100 100 | 36 | AF42 | Medium | 100 – Flash Override |
| 100 110 | 38 | AF43 | High | 100 – Flash Override |
| 001 000 | 8 | CS1 | 1 | |
| 010 000 | 16 | CS2 | 2 | |
| 011 000 | 24 | CS3 | 3 | |
| 100 000 | 32 | CS4 | 4 | |
| 101 000 | 40 | CS5 | 5 | |
| 110 000 | 48 | CS6 | 6 | |
| 111 000 | 56 | CS7 | 7 | |
| 000 000 | 0 | Default | ||
| 101 110 | 46 | EF |
Linux Systems
If you need to change this value on a Linux machine (for user data packets), it would be enough to make the declaration via QoS parameters in your DataWriter:
|
1 2 3 |
<transport_priority> <value>0x80</value> </transport_priority> |
And if you want to change the value of the metadata packets, it should be done by setting the following QoS parameter in your DataWriter:
|
1 2 3 |
<metatraffic_transport_priority> <value>0x80</value> </metatraffic_transport_priority> |
Windows Systems
If you need to change this value on a Windows machine, it won’t be enough to make the change in the QoS profile. Instead, it is necessary to do it at the application level and it must be set by modifying a system registry:
- Open the regedit application (for example typing regedit in the “Start” button).
- Using the left side tree, navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\Tcpip\Parameters path.
- There, right click, select “New” and then “DWORD”.
- Use “DisableUserTOSSetting” for the field name and for “0” for the Value data.
- Then go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\Tcpip\Qos (if you don’t have any QoS in the tree, you can create one with right click>New>Key and enter the QoS name).
- Create a string value (Right click>New>String value) and use “Do not use NLA” for the name and “1” for the value.
- Reboot you computer.
- After your system restarts, open gpedit.msc.
- Go to Computer configuration > Windows Settings > Policy-based QoS and right click on “Create new policy”.
- Check “Specify DSCP Value” and use the desired value (for example, 8). Click “Next”.
- Check “Only application with this executable name:” and fill with Process Name (executable). Click “Next” twice.
After these steps, run your application and the DSCP value should have changed.